SEO or Search Engine Optimisation is more or less the process of making your digital content more visible and attractive to search engines. SEO needs execution on many levels but is generally focused on the creation of quality and relevant content, utilization of the right keywords, building credibility and providing good user experience.
What is SEO Search Engine Optimisation?
Search engine results are a dime a dozen. But they don’t just show up to your screen in completely random order. In a way, they are syndicated by search engine algorithms according to their relevance to the terms you used to search them.
Search engines indulge content creators and users simultaneously through its complex algorithm. This means inputs from both sides are equally important in order to match intent and content. Ideally, if you are more specific with your search terms, then you’ll get a higher likelihood of getting matching, relevant search results.
Why is SEO Important?
Imagine the internet being this gargantuan depository with all sorts of books. Then, picture yourself having your own book with cool stories that you want to or share with everyone—or maybe just with a particular group people. How do you think others will find or even know that this special book of yours exists along with millions or billions of other content in this very library?
That’s where SEO typically rises to the occasion. Making your work easy to read and integrating useful keywords can help your content jump out of the pool just enough to warrant the librarian’s attention, which in this case is the search engine. That librarian now gets to recommend your book to anyone who are searching this library using matching terms.
The Different Types of SEO
We consider three main types of SEO:
On-Page SEO
This generally involves optimising individual web pages to make it appealing to search engines. This includes working on the content structure and HTML code. This is also where you optimise keywords, URLs, headers, meta tags, internal links, images and just the overall quality of your written piece. On top of all this, it also accounts for user experience (UX), which then represents the usability of your site, like page load times and responsiveness to mobile and tablet screens.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO is not an invisible process as some might expect. In fact, off-page SEO includes tasks such as link building, social media marketing, influencer outreach, online reputation management, local SEO, guest blogging and social bookmarking. Off-page SEO complements your on-page SEO efforts by helping improve the website’s authority in the eyes of search engines.
Technical SEO
This part is focused on improving technical aspects of the website that can lead to improved performance and subsequently its likelihood of being indexed by search engines. Technical SEO leads you to go deeper in the work you started with on-page SEO by improving the overall website speed, image optimisation, responsiveness and structured data markup (Schema) across your website.
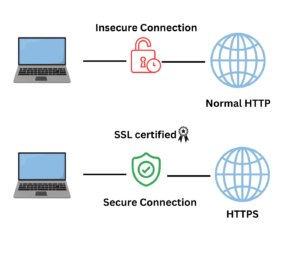
Additionally, this is where you evaluate your overall website structure, address duplicate contents, fix crawling issues and get your website that coveted SSL to signal users that browsing and transacting on your website are all done in secure connection.
What is SEO and How Does it Work?
SEO is essential so that search engines discover content from your website that you think are most relevant to your prospective audience. If you don’t put effort in SEO, then you are virtually forfeiting your place in organic search results.
Your friends may find your content by sheer familiarity and association, but your audience will have significantly reduced opportunities to grow. People who might otherwise love your work or are interested in your products will have trouble finding you if the search engine itself is having a hard time finding and categorising your website. If you want to use Google or other major search engines to potentially reach a wider audience, then it’s important that you work on your website’s SEO.

How to Do SEO for Beginners?
Learning SEO for the first time takes effort, but the repeatability of the process and its consistency in yielding results make it worthwhile.
Start with SEO Keyword Research
Keyword research is an integral part of SEO. The good news is that Google, the most recognisable search engine offers allows everyone to register and use its free Keyword Planner tool that helps users in discovering relevant keywords by simply entering terms related to the content of their website.
This free tool also helps in generating keyword ideas and introduces metrics, which measure the viability of keywords. Using Keyword Planner along with Google Search Console, which is another free web service from Google, can help website owners implement a deeper strategy in optimising content and measuring website performance.
Create Content Targeting the Keywords
Once you have relevant keywords for your website, the next step is creating content around those keywords. Targeting these keywords will give your website a better chance to rank in these search terms, likewise improving your visibility to the audience who are specifically looking for what you have to offer.
Insert Your Keywords
Inserting keywords into your content needs a strategic approach. Certain sections of your content will benefit most from keywords like the title of an article or the URL.
Additionally, you should use your primary keyword in the meta description tag of your article, image alt texts, and in the conclusion of your post. Adding an internal link to the keyword pointing to a related copy within your website will also serve as a signal to search engines that you are optimizing for that particular topic.
Just a reminder that SEO is relative to search engine marketing trends and rarely a directive from Google or other search engines.
SEO Title
“SEO title” and “page title” are often used interchangeably to a fault. SEO title is the title that is displayed in search results and can be customised along with your post’s meta description. It’s important to always use your primary keyword when creating your SEO title.
Page Title
The page title is the title that users will see when they visit your post. Similarly, your article will benefit from having your keyword inserted in the page title.
Headings
It’s also recommended to have your keyword appear once in the introduction of the post and occasionally in its headings. Using a variation of your keyword across the article is also standard practice.
Image Alt Text
The images associated with the article can be searched separately, so it’s recommended optimising them by inserting your primary keyword in their alt text. Alternative text is a descriptive attribute added to the image to provide alternative text for visually impaired users.
Image File Name
Image file names are another part of the post that must be optimised with your primary keyword. Don’t forget to only use related images on your posts to avoid confusing search engines and readers.
URL
Also, don’t forget to insert your primary keyword when crafting your URL.
Meta Description
Additionally, you should use your primary keyword in the meta description tag of your article. More importantly, craft a well-meaning and compelling meta description that makes an accurate summary or representation of your post. The meta description is one of the first things users see in search results when they come across your content.
Optimise Your Title and Meta Description for Search Engines
Optimising your title and meta description is one of SEO’s enduring best practices. But aside from inserting the primary keyword of your post, you should also aim to make the title and meta description compelling. If you’re working on a title, try to keep it around 50 to 60 characters to ensure that it displays well on search results. You can also include your brand in the meta title if brand recognition is essential to your website or project.
Add Internal and External Links
Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page of your website to another related page or topic. Ideally, you want to anchor these links to the primary keyword of the post you are linking from.
On the other hand, external links are outbound links going to another website. Likewise, these links should improve user experience and provide them with relevant results. External links must point to reputable sources to enhance your content and website’s credibility.
How Can I Do SEO for My Website?
 Learning how search engines work and incorporating some of the SEO best practices we’ve listed above will help you get started with basic SEO. However, don’t forget that creating quality and relevant content for your audience is just as important as structuring your website for search engines.
Learning how search engines work and incorporating some of the SEO best practices we’ve listed above will help you get started with basic SEO. However, don’t forget that creating quality and relevant content for your audience is just as important as structuring your website for search engines.
As a beginner, you should also take advantage of Google’s free web services like Keyword Planner and Google Search Console to monitor and measure the performance of your website. Just remember that SEO is an ongoing process and results may take time to become apparent.
But if you need assistance in accelerating your website’s growth and evaluating your progress, you can also seek help from an SEO specialist like Web9 for all your SEO and content marketing needs.